Ever since the debut of the Intel 8086 microprocessor in 1978, Intel’s x86 architecture has dominated much of the computing world.
At the time, it was revolutionary. It enabled desktop computing as we know it today and led to the server architecture that made the Internet possible. It also touched off over 40 years of exponential growth in computing power, turning Moore’s Law into reality.
However, there are some limitations inherent in the traditional binary computing that underpins today’s processors. And since as early as the 1980s, scientists have worked to find a more powerful alternative.
That alternative is quantum computing. It’s a rapidly evolving type of processing technology with the potential to fundamentally alter how we think of computing power. Here’s an explanation of what quantum computing is and the pros and cons associated with it.
What is Quantum Computing?
To understand quantum computing, you must first understand a bit about how traditional computer processors work.
At their heart, traditional microprocessors are little more than wafers of silicon with microscopic transistors printed on them.
A transistor, in electrical terms, is a type of switch. So, by leaving their transistors either powered or unpowered, computer processors can create lengthy strings of numbers consisting of ones and zeros—binary code. A one represents a powered-on transistor, and a zero is an unpowered one.
By printing huge numbers of transistors onto a single chip—today’s processors have 100 million or more—you can use the processor to do sophisticated mathematical calculations.
Those calculations form the basis of computing languages and allow computers to do the work we request of them.
Unfortunately, expanding the power of today’s processors means finding ways to print an ever-greater number of transistors onto a single chip, and there are physical limits to the process.
The only alternative would be to find a way to allow those transistors to have more than two states. That’s precisely what quantum computing aims to accomplish.
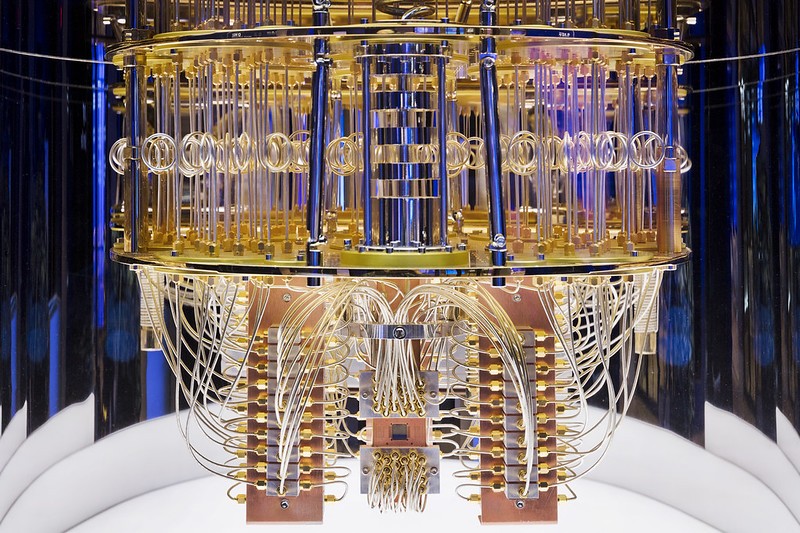
Instead of physical transistors, quantum computers instead rely on qubits, which are elemental particles—typically photons or electrons—that allow for something called superpositions.
That means they can exist simultaneously in multiple states at once.
In other words, a processor relying on qubits could do far more complex mathematical calculations than a binary processor because it wouldn’t be limited to combinations of ones and zeros.
Plus, it could equal the computing power of today’s best traditional processors with far fewer qubits than the equivalent transistors.
Let’s now discuss some advantages and disadvantages of quantum computing technology.
Some Pros of Quantum Computing
Although the field of quantum computing is still in its infancy, it’s already obvious that it’s an approach that comes with some massive advantages over traditional computing technology. The following are a few of the most important advantages.
The Ability To Handle Complex Problem Solving Faster
The most obvious advantage of quantum computing is its capacity to create sheer mathematical computing power.
That means quantum computers can carry out much more complicated tasks faster than any other known computing technology. That makes quantum computing a potential successor technology to the binary processors we’ve depended on for the past 50 years.
The Ability To Run Complex Simulations
One of the biggest limitations imposed by today’s computers is that they’re not powerful enough to handle extremely complex simulations.
To tackle some of humanity’s most cutting-edge scientific problems—like developing the advanced physics theories required to understand our universe, for example— would take an impossibly long time.
With quantum computers, however, those timescales shrink to a more manageable level. That means quantum computers may hold the keys to the development of things like high-end virtuality systems, self-aware AI systems, and much more.
It’s Well-Suited for Solving Optimization Problems
Optimization problems involve evaluating multiple solutions to a given problem to decide which one offers the greatest benefits within a given set of criteria.
They’re one of the most difficult types of problems we call on computers today to solve. And today’s computers aren’t great at solving them.
Take, for example, the recent global supply chain disruptions created by the COVID-19 pandemic. Today’s computer-controlled logistics systems couldn’t cope with the changes wrought by the virus, nor could they foresee that type of event to pre-plan for it.
Quantum computers, though, are excellent at optimization problems. They can store and evaluate more variables simultaneously and the speed to do so without imposing unacceptable time penalties.
That could allow them to enable things like more efficient supply chains that contain sufficient resiliency to meet potential crises.
It Can Speed up Drug and Materials Development
Quantum computers—due in large part to their ability to run complex simulations—may also speed up things like drug discovery and materials research.
This is because they can simulate the effects of multiple types of chemical compounds, molecules, and proteins at once to identify promising new pharmaceutical candidates.
They can also help scientists to perform simulations that aid in materials science and research. That should make the discovery and refinement of new materials faster and reduce the waste and manual labor involved in the process.
It Offers Benefits to the Financial Sector
Another area where quantum computers may have a revolutionary impact is within the world of finance. Although not widely known, financial institutions have long applied the principles and laws of physics to some of the industry’s most complex issues.
A classic example of this is the use of the concept of Brownian Movement to inform the Black-Scholes-Merton model that predicts futures pricing.
That link between physics and finance could make quantum computers a boon to the latter, helping financial institutions make decisions and transactions faster and less error-prone.
Some Cons of Quantum Computing
It’s important to realize that quantum computing, for all its promise and potential, isn’t perfect. It comes with some significant disadvantages, too.
Some of them may eventually find solutions as the technology continues to advance. Others may be a permanent roadblock to the use of quantum computing. Here’s what those disadvantages are.
Quantum Computers Might Be Able To Break Current Encryption Algorithms
The first disadvantage associated with quantum computers isn’t with the technology itself, but rather with the effect it may have on our existing computing infrastructure.
It’s that quantum computers may render all of our existing encryption algorithms obsolete. This is because today’s encryption relies on the use of sophisticated mathematical equations to function.
So sophisticated, in fact, that today’s most powerful computers couldn’t guess their way to a solution in a practical amount of time.
Quantum computers, however, could make short work of those equations owing to their sheer computing power.
If that were to happen, the security underpinnings of the internet and every protected computer system would become useless. This doesn’t mean that a new, quantum-safe encryption method is impossible, but it would take significant time and resources to implement.
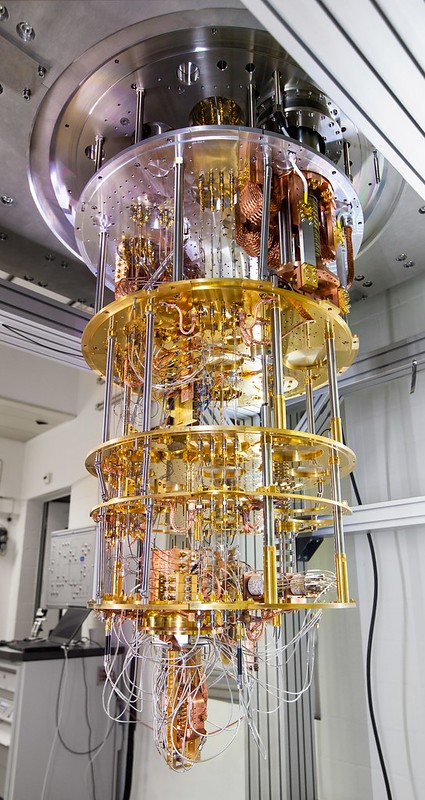
Quantum Computers Are Expensive and Difficult To Build
Another major disadvantage of quantum computing is that the machines that make it possible are extraordinarily difficult to build and costly.
The reason is that the photons and electrons that power them aren’t easy to corral and control. They’re quite delicate and susceptible to external forces.
This means they require tightly-controlled environments to function. Even when that’s possible, scientists still struggle to maintain the conditions necessary for quantum computing to work. In fact, this is the singular issue holding quantum computing, as a research field, back right now.
It Has Limited Applications
Although they’re quite powerful, it’s also true that quantum computers aren’t suitable for every computing task.
For example, while they are excellent at running complex multivariate simulations, they don’t excel at things like trigonometric functions, factoring, and nested function calls.
And while that may seem like a short list, those things are at the very heart of some of the most important tasks that today’s computers now perform for us. In fact, running any of today’s programs on a quantum computer will require a complete logic redesign. In some cases, it won’t ever be practical or cost-effective to do that.
It’s Quite Error-Prone
Lastly, quantum computers are extraordinarily error-prone. This is due to the sensitivity of the protons and electrons that power them.
With today’s technology, keeping qubits in a controlled state over lengthy periods is all but impossible. This means that qubits, if left alone for too long, will change state on their own and introduce errors into the computing process.
Right now, researchers are continuing to design error correction functions to account for this. However, a complete solution is still a long way off.
The Quantum Computing Future
Today, it’s quite obvious that quantum computing will play a major role in the future of a variety of industries, applications, and technology.
However, it’s impossible to tell when it will mature to the point where it can fulfill its potential. For now, scientists and researchers continue looking for solutions to some of quantum computing’s thorniest problems.
And in the meantime, the dream of a complete quantum computing future will have to wait. For how long, though, is anybody’s guess.
Leave a Reply